Introduction to Furnace Ignitors
In the heart of every modern home heating system lies a crucial component often overlooked until it malfunctions – the furnace ignitor. This small yet vital part plays a pivotal role in ensuring our homes remain warm and comfortable during the colder months. But what exactly is a furnace ignitor, and how does it function within the heating system? Understanding the mechanics and importance of furnace ignitors is essential for every homeowner, as it is the key to maintaining a warm and efficient home.
Identifying a Faulty Furnace Ignitor
The first step in furnace ignitor troubleshooting is recognizing the signs of a malfunction. A faulty ignitor can manifest in several ways, but two common symptoms stand out: furnace short cycling and the ignitor not glowing. Short cycling refers to the furnace turning on and off repeatedly in quick succession, a clear indication that something is amiss. On the other hand, a non-glowing ignitor, especially in modern furnaces with electronic ignition, suggests a failure in the ignition process. These symptoms not only hinder the furnace’s ability to heat your home but also signal potential safety issues.
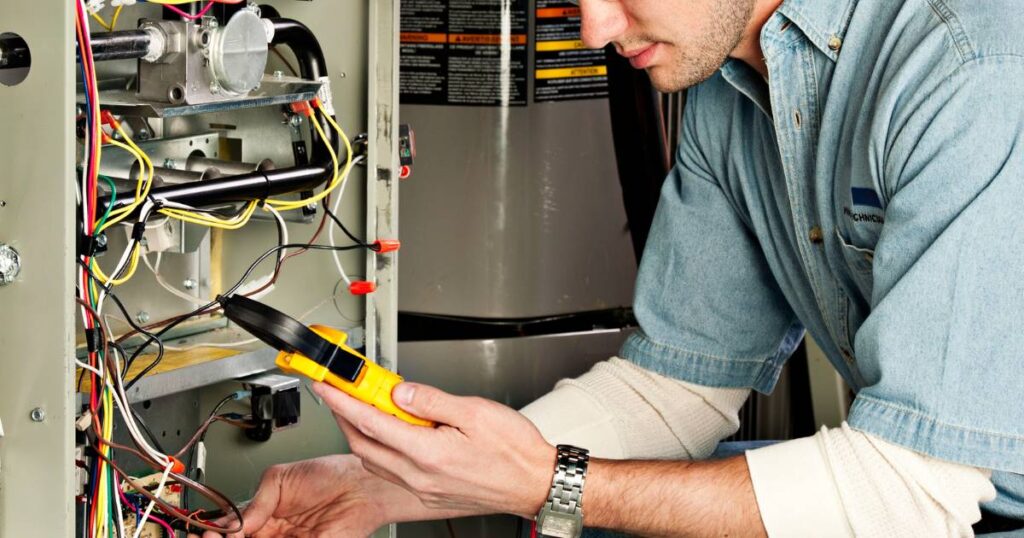

Common Causes of Furnace Ignitor Malfunction
Several factors can lead to furnace ignitor failure, and understanding these can help in quick diagnosis and repair. Some common causes include:
- Electrical Issues: Problems with the home’s electrical system or the furnace’s internal wiring can prevent the ignitor from functioning correctly.
- Dirty Ignitor: Over time, ignitors can accumulate dirt and debris, hindering their ability to ignite the gas efficiently.
- Age and Wear: Like any other component, furnace ignitors are subject to wear and tear. An ignitor typically has a lifespan of about five years, after which it may require replacement.
- Improper Voltage: Issues with the furnace’s control board can lead to incorrect voltage being supplied to the ignitor, affecting its performance.
Understanding these causes can help homeowners identify whether the issue lies with the ignitor or another part of the furnace.
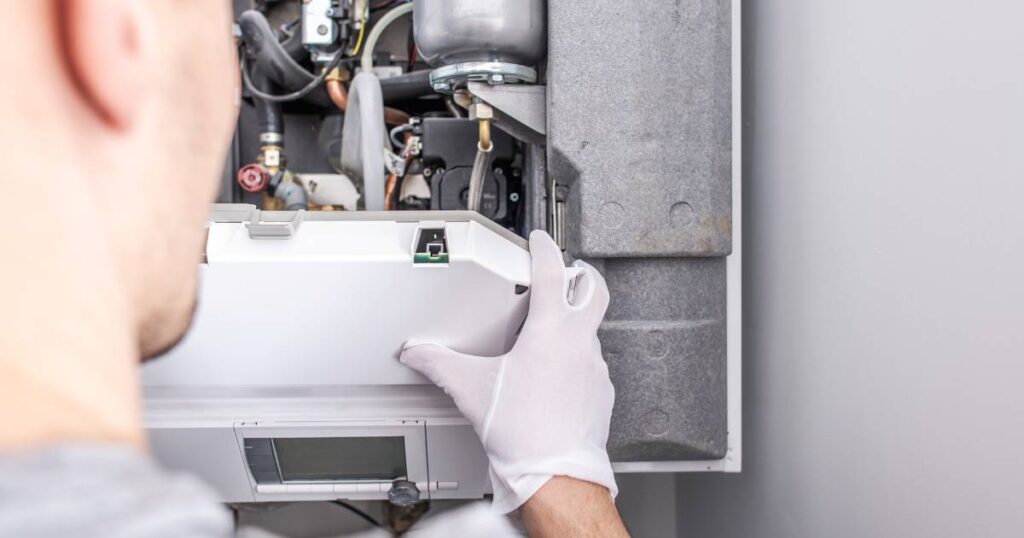

Steps to Clean and Maintain a Furnace Ignitor
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your furnace ignitor. Cleaning the ignitor is a delicate process but can be undertaken as a DIY project. The process involves:
- Powering Down: Ensure all power to the furnace is turned off to avoid any accidents.
- Accessing the Ignitor: Carefully remove the furnace cover and locate the ignitor.
- Cleaning Process: Using an emery cloth, gently clean the ignitor, being careful not to damage it. Avoid touching the ignitor with bare hands as oils from the skin can cause damage.
- Reassembly and Testing: Once cleaned, reassemble the furnace and test the ignitor by turning on the furnace.
This routine maintenance can significantly extend the life of your furnace ignitor and improve the overall efficiency of your heating system.
Testing the Furnace Ignitor
If cleaning doesn’t resolve the issue, testing the ignitor with a multimeter can help determine if it needs replacement. To test the ignitor:
- Safety First: Ensure the furnace is powered down and cool to the touch.
- Removing the Ignitor: Carefully disconnect the ignitor, taking note of its placement and connections for reassembly.
- Conducting the Test: Using a multimeter, check the ignitor’s resistance. A reading that deviates significantly from the norm indicates that the ignitor is faulty and needs replacement.
This simple test can save homeowners from the unnecessary expense of replacing a still-functional ignitor.
Replacing a Faulty Furnace Ignitor
When replacement becomes necessary, homeowners face the choice between a DIY project and professional assistance. Replacing a furnace ignitor involves:
- Identifying the Correct Replacement: Refer to the furnace’s manual to find the correct ignitor model.
- Installation: Carefully remove the old ignitor, avoiding touching the new ignitor’s surface, and install the new one in its place.
- Testing: After installation, test the furnace to ensure the new ignitor functions correctly.
While DIY replacement can be more cost-effective, it requires a certain level of technical skill and confidence. In contrast, professional replacement, though more expensive, comes with the assurance of expert handling.
Cost Analysis: DIY vs. Professional Replacement
The cost of replacing a furnace ignitor varies depending on whether you opt for a DIY approach or professional service. DIY replacement can cost between $30 to $50 for the ignitor itself. However, if you choose professional installation, the total cost, including labor, can range from $150 to $250. The decision between these two options should consider not only the cost but also the complexity of the installation and the homeowner’s comfort with DIY projects.
Conclusion: Ensuring Efficient Furnace Operation
In conclusion, the furnace ignitor is a small but essential component of your home heating system. Regular maintenance, timely cleaning, and proper testing can prevent many common issues associated with furnace ignitors. Whether you choose to replace a faulty ignitor yourself or seek professional help, understanding its function and care is crucial for maintaining an efficient and safe heating system in your home. Remember, a little attention to your furnace ignitor goes a long way in ensuring a warm and comfortable home during the cold months. Check Attic Crew furnace repair service.



